If it’s been a while since you’ve bought portable flash memory, you might be surprised by the broad availability and affordability of high-speed and large capacity microSD and SD cards. Commonly used to expand the storage in devices ranging from phones to drones and cameras, microSD cards are more frequently purchased than any other SD form factors, although full sized cards remain popular among professional camera owners.
With this guide, we’ll break down what all the different codes and ratings mean, and offer the best choices for a range of categories.
TL;DR: The Highlights
SD Card Basics: Size & Storage
All SD cards (short for Secure Digital), regardless of their size, use one or two small NAND flash memory chips — similar to those found in USB memory sticks and SSDs — and a tiny processor to manage the flow of data and instructions.
There are 3 standards for the dimensions, and they are incompatible with each other. In other words, a miniSD card reader won’t work with microSD cards (unless you use an adapter):
- Standard SD cards: 1.26 x 0.94 x 0.083 to 0.055 inches (32 x 24 x 2.1-1.4 mm)
- miniSD cards: 0.85 x 0.79 x 0.055 inches (21.5 x 20 x 1.4 mm)
- microSD cards: 0.56 x 0.43 x 0.039 inches (15 x 11 x 1 mm)
Standard SD cards all come with a small locking toggle, that enables/disables the ability to write or delete data on the card; however, mini and microSD cards don’t have this. There’s also a further 5 categories within the size classes, that indicate the connection system and data capacity of the card:
- SD or SDSC (Secure Digital Standard Capacity): maximum storage of 2 GB
- SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity): More than 2 to 32 GB of storage
- SDXC (Secure Digital Extended Capacity): More than 32 GB to 2 TB of storage
- SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity): More than 2 to 128 TB of storage
The fifth category, Secure Digital Input Output (SDIO), are special in that they contain more than just storage. These cards sport an extra device that provides additional functions, such as a Bluetooth or GPS receiver. Because there is a big difference in the storage sizes, each category also has restrictions of the file format used.
SDSC is restricted to FAT12, FAT16, and FAT16B. SDHC is nearly always FAT32 and the XC/HC versions use exFAT. The exFAT file format was specifically designed for NAND flash devices and is likely to remain the standard for many more years.
SDSC, SDHC, and SDXC cards are supported in a wide range of devices, such as laptops, smartphones, drones, and digital cameras. The need for increased storage continually grows, thanks to bigger games, more complex apps, and cameras sporting ever higher resolutions — but there will always be an SD card for everyone’s needs and budget.
SDUC is still very new, so it will be some time before we see produces routinely supporting it; 128 TB of storage should be enough for the majority of users for years to come!
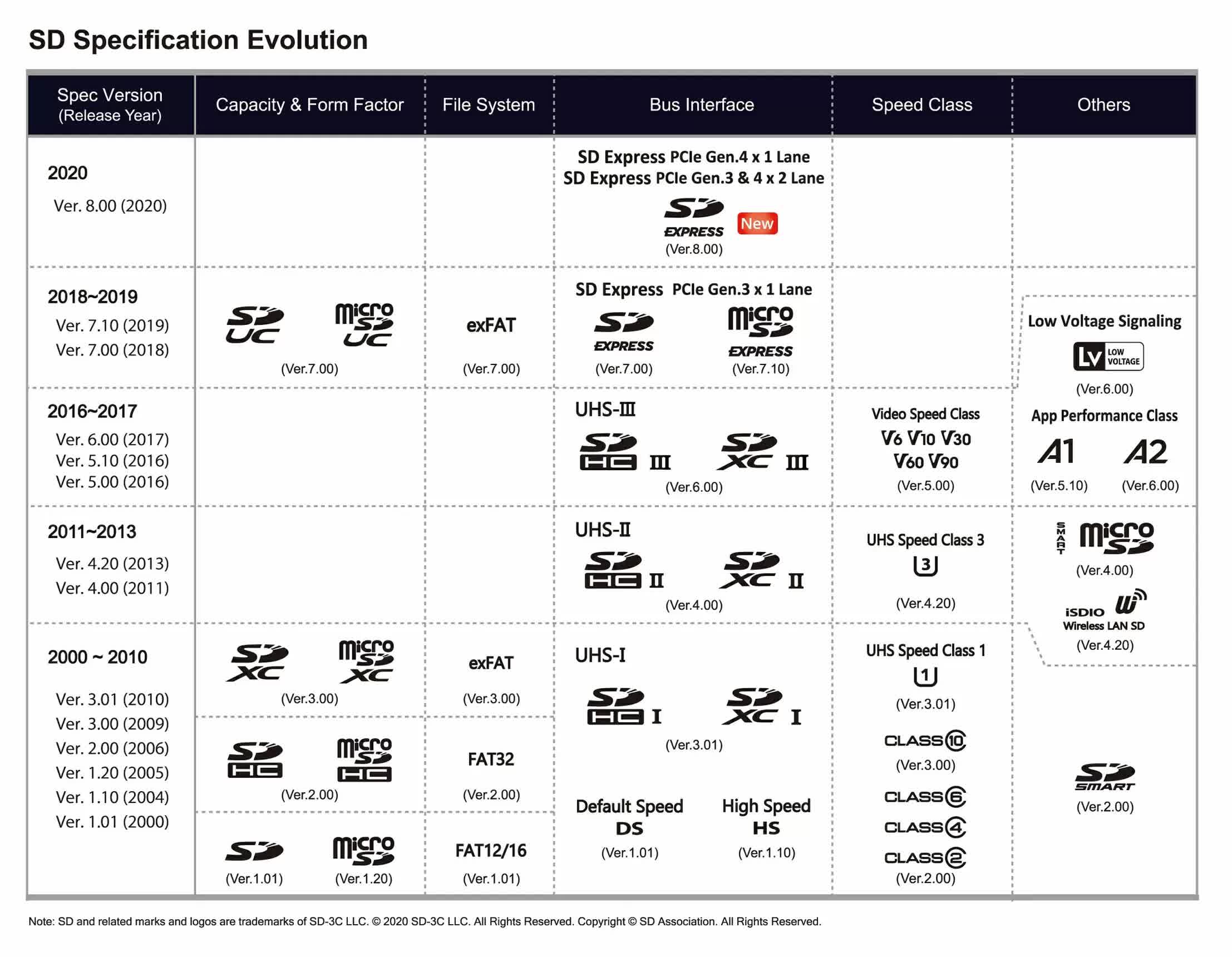
The table above, from the SD Association, shows how the Secure Digital technology has changed over the past two decades and highlights just how quickly they grew in storage capacity. You’ll probably have also noticed that there’s even more to SD cards than just capacity: time to talk about performance.
SD Card Performance: Speed Classes
All SD cards use the little brass contacts at the end of the package to receive and send information, in the form of instructions and data. The interface between the card and the reading device has evolved with each specification revision — in some cases, the updated system just runs faster (i.e. the bus clock is higher) but in some cases, the SD card has extra contacts to provide more channels for the data.
The differences between all the interfaces and performance are set out in so-called speed classes, and each one is generally organized by the peak bus throughput. This is a measure of the maximum amount of bytes per second that can be transferred between the SD card and host device.
However, not all NAND flash chips are the same, so the speed classes also indicate the minimum sequential write rate — the slowest speed at which data can be put onto the memory chip in a structured, rather than a random, way.
With so many speed classes to get your head around, it can be tricky to figure out what rating you really need. In the table below, we can see how they roughly compare.
Speed Classes
| Speed Class | Min. Seq. Writes (MB/s) | UHS Speed Class | Video Speed Class | Ideal Workload |
| Class 2 (C2) | 2 | Standard definition recording and playback | ||
| Class 4 (C4) | 4 | 720p/1080p video | ||
| Class 6 (C6) | 6 | Video Class 6 (V6) | 720p/1080p, some 4K video | |
| Class 10 (C10) | 10 | UHS Class 1 (U1) | Video Class 10 (V10) | 720p/1080p/4K video |
| 30 | UHS Class 3 (U3) | Video Class 30 (V30) | 1080p/4K video @ 60/120 fps | |
| 60 | Video Class 60 (V60) | 8K video @ 60/120 fps | ||
| 90 | Video Class 90 (V90) | 8K video @ 60/120 fps |
The SD Association came up with the speed classification systems to help differentiate what cards are best suited to what purposes. The simple Class number is the most immediate indicator to the speed of an SD card, with Class 2 (2 MB/s) cards being toward the bottom of the spectrum and are best geared towards less demanding tasks, such as recording standard definition video.
At the other end of the scale, Class 10 (10 MB/s) cards are capable of recording or playing up to 4K video, although not at a very high frame rate.
Some SDHC and SDXC cards will also support Ultra High Speed (UHS) classification, which offers improved data transfer rates. There are 3 versions of this system and the first versions to appear (UHS-I and UHS-II) offer two speed modes: U1 and U3. The former is essentially the same as C10, but U3 provides three times greater throughput at 30 MB/s — good enough for 4K videos at a high frame rates.

With SD Specification 5.0, the association provided another rating system: Video Speed. This classification is better at conveying its information, with Video Class 10 (V10), for example, applying to cards that have a minimum sequential write speed of 10 MB/s, through to Video Class 90 (V90 = 90 MB/s). At that speed, the playback and recording of 8K video at 60 to 120 fps becomes feasible.
In 2017, a faster UHS-III was released, which further improved the performance of the data bus, and in 2018, the SD Association announced the SD Express specification — this version uses up to 2 PCI Express lanes to provide a huge increase in throughput.
SD Card Bus Speeds
| Bus system | Peak throughput (MB/s) | PCI Express type | SD card supported | |
| Default speed (DS) | 12.5 | Not used | All | |
| High Speed (HS) | 25 | Not used | All | |
| Ultra High Speed I (UHS-I) | 50 | 104 | Not used | SDHC, SDXC, SDUC only |
| Ultra High Speed II (UHS-II) | 156 | 312 | Not used | SDHC, SDXC, SDUC only |
| Ultra High Speed III (UHS-III) | 312 | 624 | Not used | SDHC, SDXC, SDUC only |
| SD Express | 985 | 1969 | PCIe 3.1 (x1 or x2 lanes) | SDHC, SDXC, SDUC only |
| SD Express | 1969 | 3984 | PCIe 4.0 (x1 or x2 lanes) | SDHC, SDXC, SDUC only |
UHS-I cards have just one set of contacts for sending and receive information, so when running at the higher speed, the bus will run in what is called Half Duplex mode: the SD card will only be able to receive or send data, at any one time.
The later versions of UHS sport extra contacts, which permits Full Duplex (send and receive together), both to occur at the same time; however, in UHS-II this results in the bus being forced to run at the slower speed. UHS-III and SD Express don’t have this problem, and always run Full Duplex.
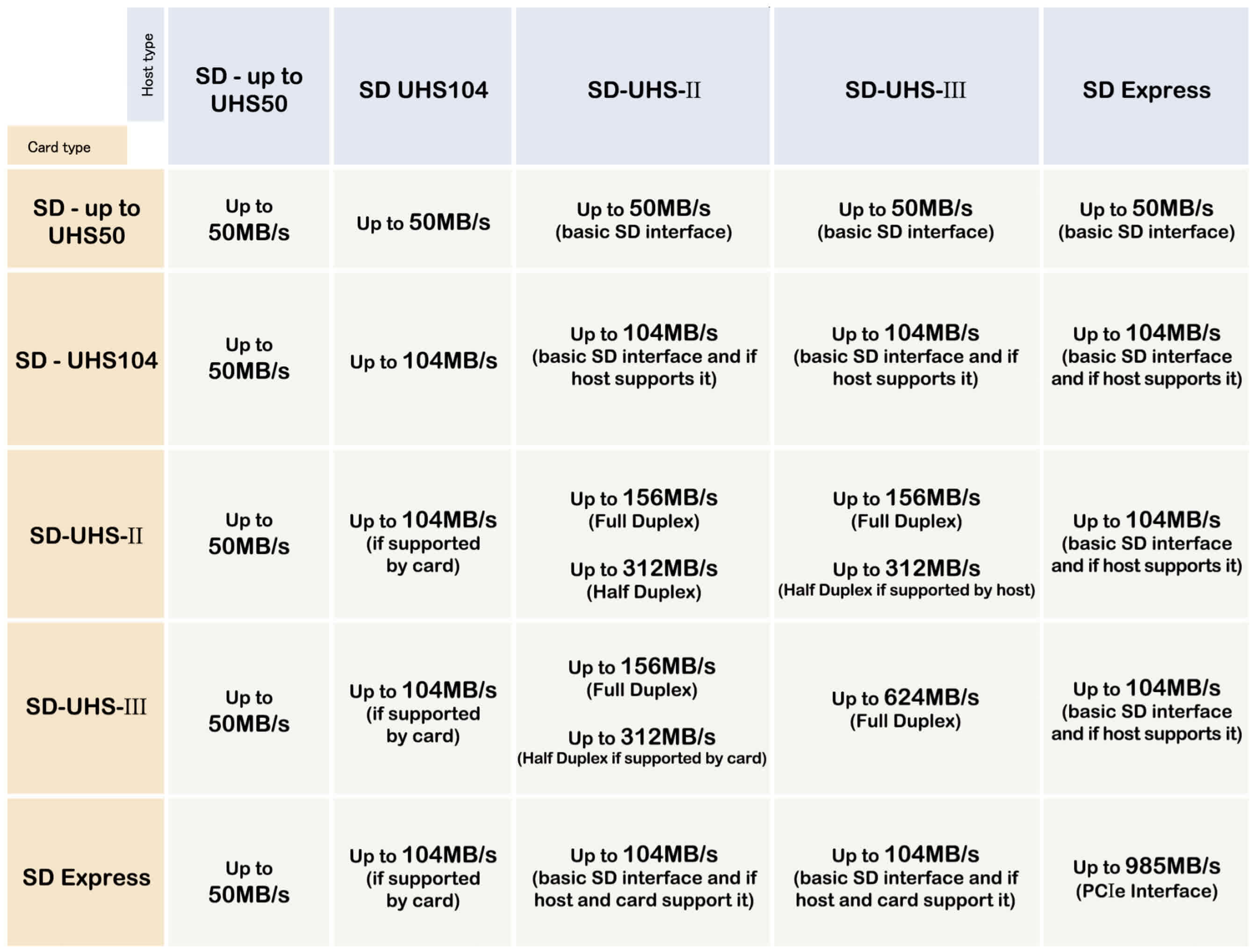
At this present time, SD cards utilizing UHS-III or SD Express aren’t anywhere to be seen on the market, despite the technologies being available for several years. But this is because the performance is only unlocked if the device using the card fully supports it. The table below shows how various cards will function in different UHS card readers, and indicates how SD Express would compare.
Not shown in the very first table is yet another category rating. The increased use of SD cards in smartphones and tablets, where the additional NAND flash can be used as working storage, requires more than just good throughput.
The ability to handle lots of random data instructions (measured in IOPs, input/output operations per second) is key to ensuring consistent system performance, and in 2015 the SD Association created two further standards: Application Class A1 and A2.
Cards rated A1 are capable good for a random read performance of 1500 IOPS and random writes of 500 IOPS, while A2 significantly increases that, although this does require very specific hardware support. Additionally, the A1/A2 rating also means that the cards offers a sustained sequential write speed equal to that of V10.
| Class | Min. Seq. Writes | Min. Random Read | Min. Random Write | Ideal Workload |
| A1 | 10 MB/s | 1500 IOPS | 500 IOPS | Editing and updating application data, not just storage |
| A2 | 10 MB/s | 4000 IOPS | 2000 IOPS | Specialized uses of the above |
All of this makes the rating system somewhat of a minefield to navigate, but generally speaking, it can be broken down into 3 simple categories: general use/value for money, best possible performance, and maximum storage capacity.
For example, a smartphone will only need something from the first category, whereas a high end camera or video recorder, used by a professional photographer, will want to consider something from the other two.
What to Buy
Although this guide should have equipped you with the information you need to pick your own SD or microSD card, we went ahead and chose models for the three categories that stood out as offering the best combination of specification and price.
Since our last update to this guide, the most notorious difference is in capacity and value, you can now buy much larger memory cards for relatively less.
Best Value microSD Card
Best Value SD Card
You may have noticed Samsung’s dominance in the flash drive market is not limited to high-speed SSDs and there’s a good chance that the company’s memory chips are in your phone, too. Thus, it shouldn’t come as a surprise to see a Samsung-branded microSD cards listed here.

For only $26, the 256GB Evo Select (UHS-1, U3) offers up to 130 MB/s reads (writes should be at least reach half that) and ships with an SD card adapter. You can also chose a card with less capacity if you want, the same Samsung card with 128GB is down to $18. There are plenty of other alternatives, but you should be aware that many are U1 cards; they advertise the same read speeds as the Samsung cards, but they have much slower writes of only 20-30 MB/s.
Best High Performance microSD Card
- Smartphone/Tablet use: SanDisk Extreme 256GB UHS-I U3/V30 A2 – $41 on Amazon
- Video recording: Lexar Professional 1066x 256GB UHS-I U3/V30 – $35 on Amazon
Best High Performance SD Card
For a wide majority of users, the best value cards will be fast enough and will offer plenty of storage. However, for more specialized use (and if top-end performance is required), make sure you are buying a card that’s right for the task, and that your device can take full advantage of the card’s rating.
If you want fast storage for a smartphone or tablet, you should be more concerned about fast random access and reading small files simultaneously. The SanDisk Extreme 256 GB is rated for faster A2 application performance (4000 read and 2000 write IOPS) and lists 160 MB/s sequential reads with 90 MB/s write speeds.
For movie recording on drones and video equipment, you want a card with the highest rating (UHS-II V90) but those are not available in the microSD format. The Lexar Professional 1066x has been rated for 4K video recording and is great value at ~$35 for 256 GB. In a previous version of this article we had also recommended UHS-II rated microSD cards but those appear to be more scarce than before (the card reader must be UHS-II rated to take advantage of the faster memory, too).
If you want the best performance on full size SD, top performing SD cards such as Lexar can reach 300 MB/s reads and better sustained writes in the larger form factor.
Best High Capacity microSD Card
Best High Capacity SD Card
- More storage: SanDisk Extreme Pro 1TB SDXC UHS-I U3/V30 – $214 on Amazon
- Good Alternative: Lexar Professional 1066x 1TB SDXC UHS-I – $215 on Amazon

If you simply need the maximum amount of storage you can get, 1TB cards are much more affordable than before. You won’t find anything bigger for the price than Lexar Play 1 TB (UHS-1, U3/V30) on the microSD side. It might seem expensive at $133 but if you are routinely shooting 4K video, then you’ll welcome the extra capacity.
On the SD format, if you need the highest capacity and storage, then it will have to be the SanDisk 1TB Extreme or Lexar’s Pro offering (both UHS-1, U3/V30, A2) — they are still an expensive affair but cost about half of what they used to just over a year ago for that kind of storage capacity.

