The Euclid space telescope, launched July 1 on a mission to shed more light on elusive dark matter and dark energy, has reached its destination orbit and on Monday its European operators revealed its first test images.
The star-filled snapshots were taken during the space telescope’s commissioning – a phase during which its powerful instruments are finely calibrated – and therefore not representative of its full potential.
But the European Space Agency (ESA) says the tests already show it will be capable of fulfilling its massive mission.
“After more than 11 years of designing and developing Euclid, it’s exhilarating and enormously emotional to see these first images,” Euclid project manager Giuseppe Racca said in a statement.
Early commissioning test image from the near-infrared spectrometer and photometer instrument. (ESA)
After blasting off from Florida, the satellite has traveled about one million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from Earth to its observational orbit.
From there, Euclid will chart the largest-ever map of the universe, encompassing up to two billion galaxies across more than a third of the sky.
By capturing light that has taken 10 billion years to reach Earth’s vicinity, the map will also offer a new view of the 13.8-billion-year-old universe’s history.
Its visible light camera will let it measure the shape of galaxies, while its near-infrared spectrometer and photometer (NISP) – developed with the help of NASA – will allow it to measure how far away they are.
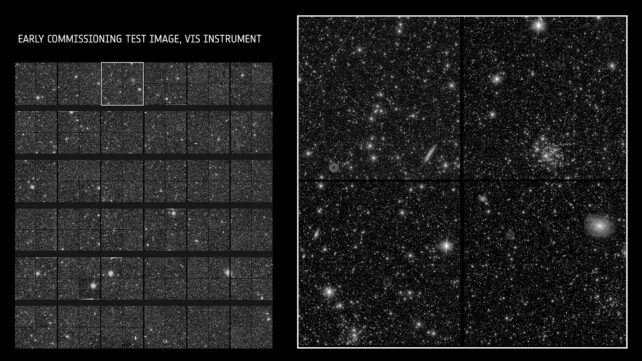 A visible light image showing the full field and then a zoomed in view for detail. (ESA)
A visible light image showing the full field and then a zoomed in view for detail. (ESA)
But when the instruments were switched on, researchers were spooked by “an unexpected pattern of light contaminating the images,” the ESA said.
An investigation led researchers to believe that “some sunlight was creeping into the spacecraft, probably through a tiny gap,” but that it was only detected when Euclid was oriented in certain ways.
“By avoiding certain angles,” ESA said, Euclid’s imaging device “will be able to fulfil its mission.”
Scientists hope to use information gathered to address what Racca previously called a “cosmic embarrassment”: that 95 percent of the universe remains unknown to humanity.
Around 70 percent is thought to be made of dark energy, the name given to the unknown force that is causing the universe to expand at an accelerated rate.
And 25 percent is believed to be dark matter, thought to bind the universe together and make up around 80 percent of its mass.
The telescope’s scientific operations are due to begin in October.
© Agence France-Presse

